
Tourism continues to be one of the sectors hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly for countries in the Asia-Pacific region and Western Hemisphere. Governments in these regions, and elsewhere, have taken measures to ease the economic shock to households and businesses, but longer-term the industry will need to adapt to a post-pandemic “new normal.”
If you are hesitant to hop on a plane these days, you are not alone. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourist arrivals are estimated to have fallen 74 percent in 2020 compared to 2019.
If you are hesitant to hop on a plane these days, you are not alone. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourist arrivals are estimated to have fallen 74 percent in 2020 compared to 2019.
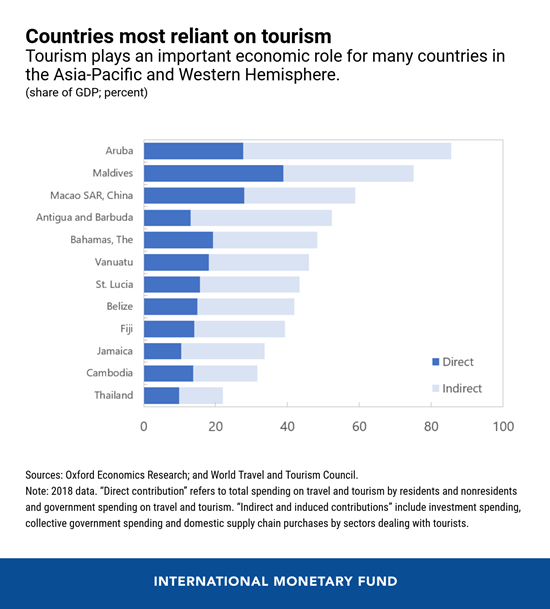
For many developing countries in the Asia-Pacific and Western Hemisphere—small island states in particular—the effects have been severe. Before the pandemic hit, tourism was big business, accounting for more than 10 percent of global GDP. The share was even larger in tourism-dependent countries.
Toward recovery
To recover, vaccines will need to be widely distributed, and policy solutions implemented.
Some governments have been providing financial support, either directly or through soft loans and guarantees to the industry. Thailand allocated $700 million to spur domestic tourism, while Vanuatu offered grants to small and medium-sized enterprises. Countries have also been assisting firms to adapt their business models and retrain staff. In Jamaica, the government gave free online training certification classes to 10,000 tourism workers to help improve their skills.
However, many tourism-dependent economies are hampered by limited fiscal space. New initiatives to reignite the sector could perhaps help. In Costa Rica, for example, national holidays have temporarily been moved to Mondays to boost domestic tourism by extending weekends. Barbados introduced a ‘Welcome Stamp’ visa—a one-year residency permit that allows remote employees to live and work from the country. Similarly, Fiji launched a Blue Lanes initiative that allows yachts to berth in its marinas after meeting strict quarantine and testing requirements.
Post-pandemic, a continuing shift toward ecotourism—a fast-growing industry focused on conservation and local job creation—could give an additional boost to the industry. This is already a key element of Costa Rica’s tourism strategy. Thailand too is trying to shift to niche markets, including adventure travel and health and wellness tours.
Technology can also play an important role. With social distancing and health and hygiene protocols likely to remain in place for the foreseeable future, touchless service delivery and investments in digital technology could be a bridge to recovery.
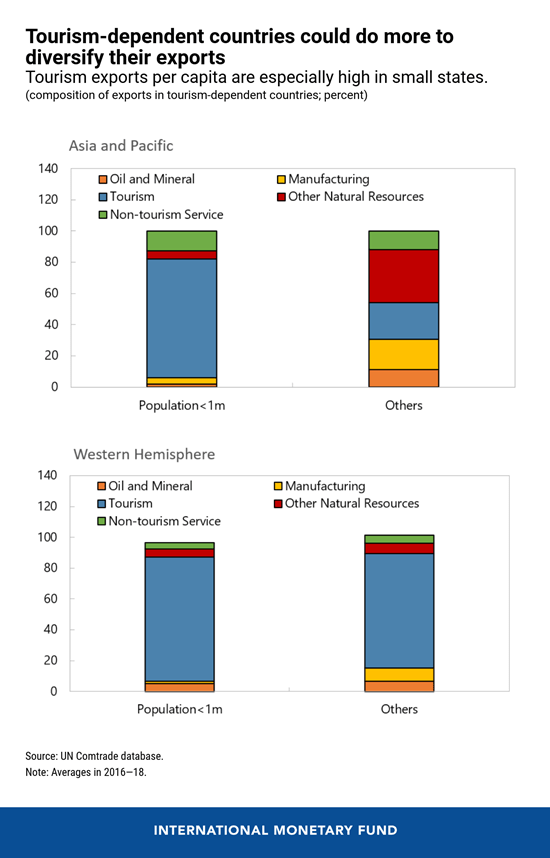
Finally, should the reduction in travel be longer lasting, owing to changes in tourist preferences or economic scarring, some tourism-dependent countries may need to embark on a long and difficult journey to diversify their economies. Investing in non‑tourism sectors is a long-term goal but could be aided by strengthening links between tourism and locally produced agriculture, manufacturing, and entertainment. In Jamaica, for instance, an online platform was launched that allows buyers in the hotel industry to directly purchase goods from local farmers. Exports, including services, could also be expanded, using regional agreements to address the constraints imposed by limited economies of scale.
Solutions will differ from country to country, and the pace and scope of recovery will of course depend on global developments. But there is an important opportunity to be harnessed. Beyond the immediate priority of mitigating the impact of the pandemic, countries will need to create a “new normal” for the tourism industry. Diversifying, shifting to more sustainable tourism models and investing in new technologies could help to shape the recovery.